| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- dfs
- c++
- C#
- 프로그래머스
- 플레이어 이동
- 백준 17070번
- 유니티
- Lv.3
- 2870번 수학숙제
- 오브젝트 풀링
- 백준 1103번 게임
- 백준 c++ 2468번
- 수학숙제
- 17070번
- 백준 c++ 2870번
- 백준 1103번
- Beakjoon
- 백준 1103번 c++
- 2870번
- 코테
- Lv2
- 백준 2870번
- 2870번 수학숙제 c++
- 백준
- 2870번 c++
- 코딩테스트
- Unity
- 2468 c++
- Algorithm
- 백준 17070번 c++
- Today
- Total
주녘공부일지
[백준 17070번 C++] Gold5. 파이프 옮기기 1 본문
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/17070
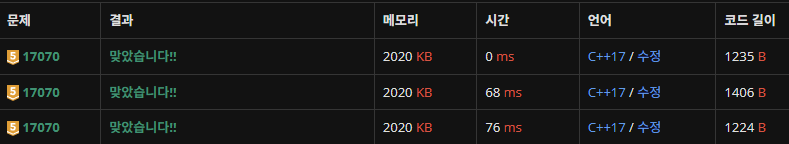
핵심 아이디어 및 정답 코드
- 파이프를 옮길 수 있는 경우의 수를 구하는 문제
- 접근 방식에 따라 DFS, DP로 풀 수 있음
맨 위에부터 DP, DFS(도착지에서 탐색), DFS(출발지에서 탐색)
1. DFS 풀이
https://godgjwnsgur7.tistory.com/47
[Algorithm C#] BFS, DFS ( + Back Tracking )
1. BFS(Breadth First Search) - 너비 우선 탐색최단 경로, 임의의 경로를 찾고 싶을 때, 등에 사용- 큐(FIFO) 사용 // 큐를 이용 public void BFS(int index) { Node root = nodes[index]; Queue queue = new Queue(); queue.Enqueue(root);
godgjwnsgur7.tistory.com
1) 출발지에서 시작
- 직관적으로 주어진 문제에 대하여 완전 탐색을 위한 깊이 우선 탐색 (DFS)을 수행
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<bool>> boolVecs;
int answer;
int maxPos;
void DFS(int posY, int posX, bool dirY, bool dirX)
{
if (posY >= maxPos || posX >= maxPos || boolVecs[posY][posX])
return;
if (dirY && dirX && (boolVecs[posY - 1][posX] || boolVecs[posY][posX - 1]))
return;
if (posY == maxPos - 1 && posX == maxPos - 1)
{
answer++;
return;
}
if (dirY && dirX)
{
DFS(posY + 1, posX, true, false);
DFS(posY + 1, posX + 1, true, true);
DFS(posY, posX + 1, false, true);
}
else if (dirY)
{
DFS(posY + 1, posX, true, false);
DFS(posY + 1, posX + 1, true, true);
}
else // dirX
{
DFS(posY + 1, posX + 1, true, true);
DFS(posY, posX + 1, false, true);
}
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
answer = 0;
cin >> maxPos;
for (int y = 0; y < maxPos; y++)
{
int temp;
vector<bool> boolVec(maxPos);
for (int x = 0; x < maxPos; x++)
{
cin >> temp;
boolVec[x] = (temp == 1);
}
boolVecs.push_back(boolVec);
}
DFS(0, 1, false, true);
cout << answer;
return 0;
}
1) 도착지에서 시작
- 출발지에서 탐색하면, 벽이 없다는 가정 하에도 도착지에 도착할 수 없는 경우의 수도 계산하게 되므로, 필요 없는 연산을 줄일 수 있음
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool boolArrays[16][16];
int answer;
void DFS(int posY, int posX, bool dirY, bool dirX)
{
if (posY < 0 || posX < 0 || boolArrays[posY][posX])
return;
if (dirY && dirX && (boolArrays[posY + 1][posX] || boolArrays[posY][posX + 1]))
return;
if (posY == 0 && posX == 1)
{
if (dirX)
answer++;
return;
}
if (dirY && dirX)
{
DFS(posY - 1, posX, true, false);
DFS(posY - 1, posX - 1, true, true);
DFS(posY, posX - 1, false, true);
}
else if (dirY)
{
DFS(posY - 1, posX, true, false);
DFS(posY - 1, posX - 1, true, true);
}
else // dirX
{
DFS(posY - 1, posX - 1, true, true);
DFS(posY, posX - 1, false, true);
}
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
answer = 0;
int maxPos;
cin >> maxPos;
for (int y = 0; y < maxPos; y++)
{
int temp;
for (int x = 0; x < maxPos; x++)
{
cin >> temp;
boolArrays[y][x] = (temp == 1);
}
}
if (boolArrays[maxPos - 1][maxPos - 1] == false)
{
DFS(maxPos - 1, maxPos - 2, false, true);
DFS(maxPos - 2, maxPos - 2, true, true);
DFS(maxPos - 2, maxPos - 1, true, false);
}
cout << answer;
return 0;
}2. DP 풀이
- DP 알고리즘을 통해 각 좌표에 대하여 도착할 수 있는 경우의 수를 합하여 도착지에 최종적으로 도착할 수 있는 경우의 수를 도출해내는 방법
1) 좌표 (y, x) 에 가로 방향으로 도착하는 경우의 수
-> (y, x - 1) 에 가로 방향으로 도착하는 경우의 수 + 대각선 방향으로 도착하는 경우의 수
2) 좌표 (y, x) 에 대각선 방향으로 도착하는 경우의 수
-> (y - 1, x - 1) 에 대각선 방향으로 도착하는 경우의 수
3) 좌표 (y, x) 에 세로 방향으로 도착하는 경우의 수
-> (y - 1, x) 에 대각선 방향으로 도착하는 경우의 수 + 세로 방향으로 도착하는 경우의 수
https://godgjwnsgur7.tistory.com/109
[Algorithm C#] 동적 계획법(DP) / Memoization, Tabulation
1. 동적 계획법(DP : Dynamic Programming) 복잡한 하나의 큰 문제를 여러 개의 작은 문제로 나누어 해결하는 문제해결 방법 중 하나 - 작은 문제의 연산 결과를 저장해놓았다가 다시 큰 문제를 해결할
godgjwnsgur7.tistory.com
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
bool boolArrays[16][16] = { false };
int dp[16][16][3] = { 0 }; // 0 가로, 1 대각, 2 세로
int length;
cin >> length;
for (int y = 0; y < length; y++)
{
int temp;
for (int x = 0; x < length; x++)
{
cin >> temp;
boolArrays[y][x] = (temp == 1);
}
}
dp[0][1][0] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < length; i++)
if (!boolArrays[0][i])
dp[0][i][0] = dp[0][i - 1][0];
for (int y = 1; y < length; y++)
{
for (int x = 2; x < length; x++)
{
if (!boolArrays[y][x])
{
dp[y][x][0] = dp[y][x - 1][0] + dp[y][x - 1][1];
dp[y][x][2] = dp[y - 1][x][1] + dp[y - 1][x][2];
if (!boolArrays[y - 1][x] && !boolArrays[y][x - 1])
dp[y][x][1] = dp[y - 1][x - 1][0] + dp[y - 1][x - 1][1] + dp[y - 1][x - 1][2];
}
}
}
int answer = dp[length - 1][length - 1][0] + dp[length - 1][length - 1][1] + dp[length - 1][length - 1][2];
cout << answer;
return 0;
}
'CodingTest > BeakJoon Gold' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 1103번 C++] Gold2. 게임 (2) | 2024.12.06 |
|---|
